- Your cart is empty
- Continue Shopping
Piston Head in a Car Engine: Role & Design

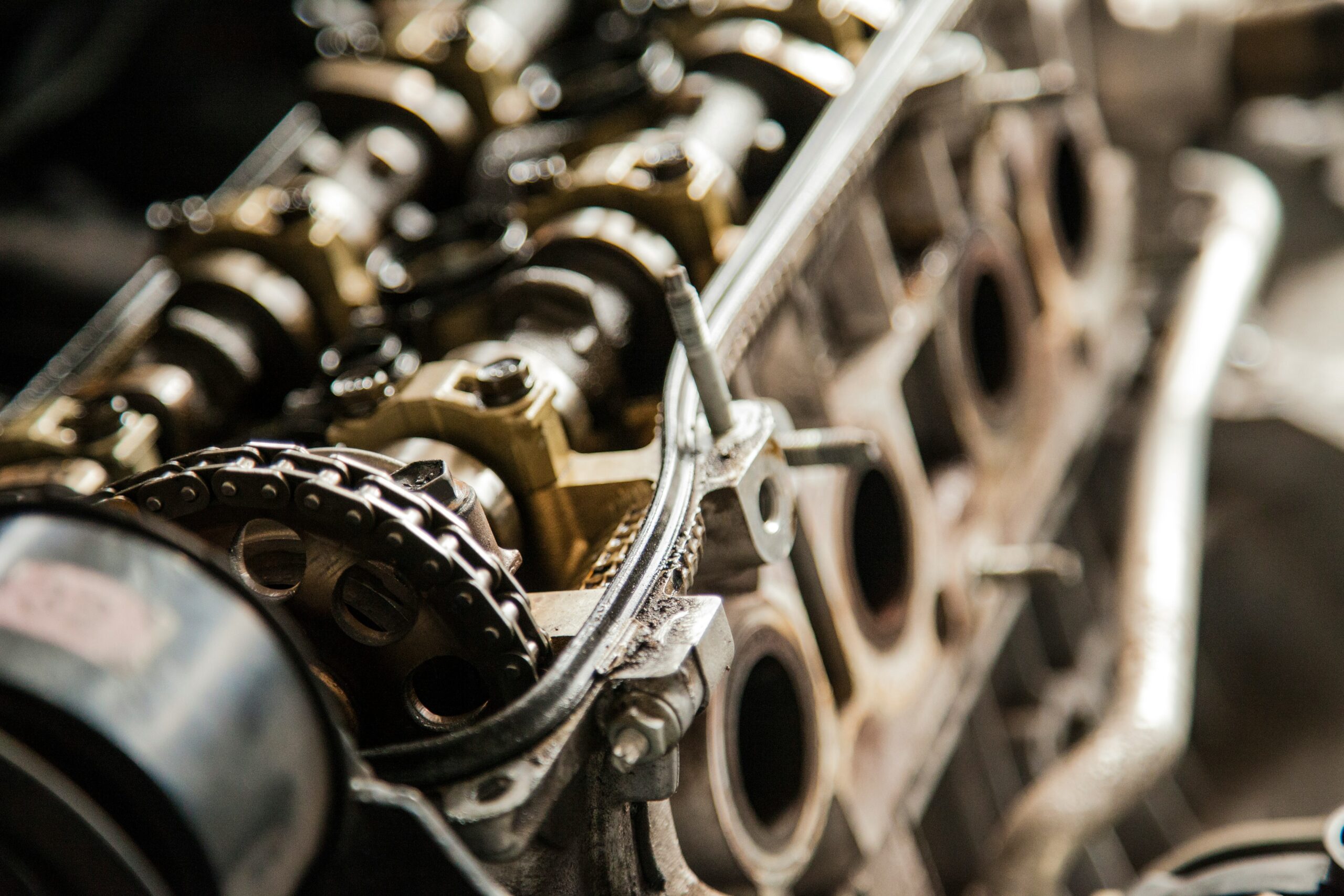
The piston head, often simply called the piston crown, is one of the most critical components of an internal combustion engine. It sits at the top of the piston, directly facing the combustion chamber, and plays a vital role in engine efficiency, performance, and durability.
What is a Piston Head?
The piston head is the top surface of the piston that comes into direct contact with the high-pressure combustion gases inside the engine cylinder. It forms part of the combustion chamber and must withstand extreme heat, pressure, and force.
Functions of a Piston Head
- Sealing the Combustion Chamber
- The piston head, along with piston rings, prevents gases from escaping the combustion chamber, ensuring efficient power generation.
- Withstanding Heat and Pressure
- During combustion, temperatures can exceed 2,500°C and pressures can rise above 100 bar. The piston head is engineered to endure these harsh conditions without deforming.
- Shaping Combustion
- The design of the piston crown influences how the air-fuel mixture swirls, ignites, and burns. This affects power output, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
- Transferring Force
- The force generated by the combustion pushes the piston head down, transferring energy to the piston rod and ultimately to the crankshaft, which powers the vehicle.
Types of Piston Head Designs
Different engines use piston heads with varying shapes depending on performance needs:
- Flat-Top Piston
- Simple design, commonly used in everyday vehicles.
- Provides balanced compression and efficiency.
- Dome Piston
- Convex shape on top increases compression ratio.
- Typically used in high-performance and racing engines for greater power.
- Dish Piston
- Concave shape reduces compression ratio.
- Often found in turbocharged or supercharged engines to prevent engine knocking.
- Recessed Piston (Valve Reliefs)
- Has small cutouts to prevent valves from striking the piston.
- Improves compatibility with high-lift camshafts in performance engines.
Materials Used in Piston Heads
Since the piston head faces extreme stress, it is made from durable materials such as:
- Aluminum alloys: Lightweight and excellent for heat dissipation; common in modern cars.
- Steel alloys: Stronger and used in heavy-duty or high-performance engines.
Common Problems with Piston Heads
- Piston Head Damage (Holes or Cracks)
- Caused by engine knocking, overheating, or detonation.
- Leads to loss of compression and power.
- Carbon Build-Up
- Deposits form on the piston crown, reducing efficiency and causing pre-ignition.
- Scuffing or Wear
- Occurs when lubrication fails or contaminants enter the cylinder.
Importance in Engine Performance
The design and condition of the piston head directly influence:
- Compression ratio
- Power output
- Fuel economy
- Exhaust emissions
This makes piston head engineering a key factor in modern engine design, especially with the rise of turbocharging, downsizing, and emission regulations.
The piston head is the heart of the combustion process in a car engine. Its design, material, and condition determine how efficiently an engine runs, how much power it produces, and how long it lasts